In this article, you will learn the basics of soil gradation and an Interactive online Excel sheet to calculate it easily with just input of the soil sieve analysis.
Why is Soil Gradation Important?
The grading of soil is very important in the field of engineering, especially in geotechnical engineering. It is a basic step for the:
- Foundation Design
- Construction Planning
- Drainage and Permeability
- Slope Stability
- Earthwork and Excavation
- Pavement Design
- Predicting Settlement
- Soil Erosion Control
- Environmental Impact Assessments
- Research and Developments
Which Criteria need to be determined?
The most important criteria for grading any soil are its coefficient of uniformity (Cu) and coefficient of curvature (Cc).
- Uniformity coefficient (Cu): It is the ratio between the sieve size which will pass 60% of the sand by weight (D60) to the effective size (D10). Cu = D60/D10. A higher Cu value indicates a wider range of particle sizes and, consequently, a less uniform soil.
- Coefficient of Curvature (Cu): It is calculated as the square of the ratio (D30)^2 / (D10 x D60), where D30 is the particle diameter at which 30% of the soil particles are finer than the specified size. Cc provides information about the shape of the gradation curve.
What does a soil look like?
The typical values are:
- Well-Graded Gravel: Cu > 4 and 1 < Cc < 3
- Well-Graded Sand: Cu > 6 and 1 < Cc < 3
If the soil does not satisfy any of the two conditions, then the soil is poorly graded.
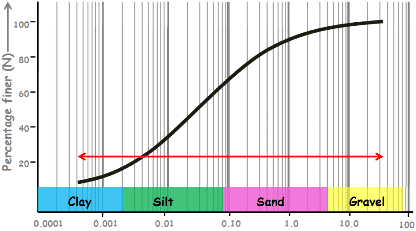
Figure: Gradation of Soil with particle diameters
Source: Link, gives the representation of soil gradation
Online Calculate the Cu and Cc

STEP 1: Choose the sheet with the number of sieves used (11,10 or 8) and Input the sieve sizes and the mass of soil retained.
That’s it. The Excel sheet will give the soil Cu and Cc and the Graph.
*Disclaimer: The author is not responsible for the professional or any use of this calculation sheet.